Following the three previous blog posts, let's continue taking tiny steps in our endeavour to create a pong game in elm.
Contribution from Rémy
Rémy is a former colleague from Mozilla and is a wonderful, very joyful and productive friend. When he saw this series of blog posts, he contributed a few issues and pull requests to the project, thanks!
The first PR is to fix a corner case where the ball would be "trapped" by the paddle: if the paddle catches the ball "too late" but still before it touches the side, the ball bounces back and forth on each frame. To fix that, the trick is to also check the direction the ball is going, and only bounce if it's going towards the side the paddle is on:
(ball.x - ball.radius <= x + width)
&& (ball.y >= y)
&& (ball.y <= y + height)
+ && (ball.horizSpeed < 0)
RightPaddle { x, y, height } ->
(ball.x + ball.radius >= x)
&& (ball.y >= y)
&& (ball.y <= y + height)
+ && (ball.horizSpeed > 0)
The second PR is a bit more involved: it's not related to the game itself, but rather to how people can interact and contribute to it.
Adding a few helper scripts is convenient to newcomers, and having a npm run
deploy helps with automating the upload to the
github pages where the most up to date
version is playable.
Now for the issues. The second one is an issue I spotted but didn't get around to fixing yet. Here's how to reproduce it:
- one player presses and keeps pressing a key (eg: the down arrow)
- as the paddle moves down, the game is restarted (because one of the two players won)
- while the game is paused (the 500ms delay), the key is released (eg: the down arrow is released)
- once the game is restarted, the paddle moves down on its own, even though the down arrow is released
The reason is pretty obvious: during the pause we're not subscribed to the
onKeyUp events so we don't update the PaddleMovement.
There's an easy way to fix that: reset the paddles (position and movement) once the game restarts:
SleepDone ->
( { model
| ball = initBall
+ , rightPaddle = RightPaddle <| initPaddle 480
+ , leftPaddle = LeftPaddle <| initPaddle 10
+ , rightPaddleMovement = NotMoving
+ , leftPaddleMovement = NotMoving
, gameStatus = NoWinner
}
, Cmd.none
Another way would have been to keep being subscribed to the key events even during the pause, but that wouldn't have been sufficient: during the pause we don't subscribe to the animation frame events anymore, and as such our "game loop" is on pause, and we don't update anything anymore. So even though we'd be registering the key presses, the paddles wouldn't be moving, which would be confusing.
So instead of changing the subscription, we'd have to do a case on the
GameStatus when updating the ball, and only update it while there's no
winner:
ball.vertSpeed
updatedBall =
- { ball
- | x = ball.x + horizSpeed
- , y = ball.y + vertSpeed
- , horizSpeed = horizSpeed
- , vertSpeed = vertSpeed
- }
+ case model.gameStatus of
+ Winner _ ->
+ ball
+
+ NoWinner ->
+ { ball
+ | x = ball.x + horizSpeed
+ , y = ball.y + vertSpeed
+ , horizSpeed = horizSpeed
+ , vertSpeed = vertSpeed
+ }
updatedRightPaddle =
updatePaddle model.rightPaddleMovement model.rightPaddle
@@ -248,10 +253,6 @@ update msg model =
SleepDone ->
( { model
| ball = initBall
- , rightPaddle = RightPaddle <| initPaddle 480
- , leftPaddle = LeftPaddle <| initPaddle 10
- , rightPaddleMovement = NotMoving
- , leftPaddleMovement = NotMoving
, gameStatus = NoWinner
}
, Cmd.none
@@ -397,16 +398,11 @@ viewScore score =
subscriptions : Model -> Sub Msg
subscriptions model =
- case model.gameStatus of
- NoWinner ->
- Sub.batch
- [ Browser.Events.onAnimationFrameDelta OnAnimationFrame
- , Browser.Events.onKeyDown (Decode.map KeyDown keyDecoder)
- , Browser.Events.onKeyUp (Decode.map KeyUp keyDecoder)
- ]
-
- Winner _ ->
- Sub.none
+ Sub.batch
+ [ Browser.Events.onAnimationFrameDelta OnAnimationFrame
+ , Browser.Events.onKeyDown (Decode.map KeyDown keyDecoder)
+ , Browser.Events.onKeyUp (Decode.map KeyUp keyDecoder)
+ ]
So we reverted our change in the SleepDone message (when we restart the
game), and we now always subscribe to all the events (animation frame and
keys). And finally we only update the ball when it's not on pause after a win.
However we now have a very weird behaviour:
Well... the game loop runs every animation frame (so roughly 60 times per second). And on each frame, even when the game is "paused" (actually, just the ball is paused now) we check if there's a win, and we increase the score, and then start a 500ms delay, but this delay doesn't prevent the score increase on the next frame as there's still a win (the ball hasn't moved).
So let's modify the current case maybeWinner updatedBall to be:
updatePaddle model.leftPaddleMovement model.leftPaddle
( gameStatus, score, cmd ) =
- case maybeWinner updatedBall of
- Nothing ->
- ( NoWinner, model.score, Cmd.none )
-
- Just player ->
+ case ( maybeWinner updatedBall, model.gameStatus ) of
+ ( Just player, NoWinner ) ->
let
alwaysSleepDone : a -> Msg
alwaysSleepDone =
@@ -195,6 +192,9 @@ update msg model =
updateScores model.score player
in
( Winner player, updatedScore, delayCmd )
+
+ _ ->
+ ( model.gameStatus, model.score, Cmd.none )
in
( { model
| ball = updatedBall
Here the case is on a 2-tuple, and the only special case that interests us is
when we have no winner in the GameStatus yet, but we just detected there's a
win. In this case, and only in this case do we increase the score and start a
500ms sleep.
In all the other cases (destructured as _ -> here) we just return the
unmodified game status, score, and no commands.
That's now working perfectly. However the code is starting to get really unreadable in this game loop... Let's see if we can rewrite and refactor it to make it clearer:
case msg of
OnAnimationFrame timeDelta ->
let
- ball =
- model.ball
-
- shouldBounce =
- shouldBallBounce model.rightPaddle model.ball
- || shouldBallBounce model.leftPaddle model.ball
-
- horizSpeed =
- if shouldBounce then
- ball.horizSpeed * -1
-
- else
- ball.horizSpeed
-
- shouldBounceVertically =
- shouldBallBounceVertically model.ball
-
- vertSpeed =
- if shouldBounceVertically then
- ball.vertSpeed * -1
-
- else
- ball.vertSpeed
-
updatedBall =
- case model.gameStatus of
- Winner _ ->
- ball
-
- NoWinner ->
- { ball
- | x = ball.x + horizSpeed
- , y = ball.y + vertSpeed
- , horizSpeed = horizSpeed
- , vertSpeed = vertSpeed
- }
-
- updatedRightPaddle =
- updatePaddle model.rightPaddleMovement model.rightPaddle
-
- updatedLeftPaddle =
- updatePaddle model.leftPaddleMovement model.leftPaddle
+ updateBall model
( gameStatus, score, cmd ) =
case ( maybeWinner updatedBall, model.gameStatus ) of
@@ -198,8 +158,8 @@ update msg model =
in
( { model
| ball = updatedBall
- , rightPaddle = updatedRightPaddle
- , leftPaddle = updatedLeftPaddle
+ , rightPaddle = updatePaddle model.rightPaddleMovement model.rightPaddle
+ , leftPaddle = updatePaddle model.leftPaddleMovement model.leftPaddle
, gameStatus = gameStatus
, score = score
}
@@ -259,6 +219,50 @@ update msg model =
)
+updateBall :
+ { a
+ | gameStatus : GameStatus
+ , ball : Ball
+ , rightPaddle : Paddle
+ , leftPaddle : Paddle
+ }
+ -> Ball
+updateBall { gameStatus, ball, rightPaddle, leftPaddle } =
+ let
+ shouldBounce =
+ shouldBallBounce rightPaddle ball
+ || shouldBallBounce leftPaddle ball
+
+ horizSpeed =
+ if shouldBounce then
+ ball.horizSpeed * -1
+
+ else
+ ball.horizSpeed
+
+ shouldBounceVertically =
+ shouldBallBounceVertically ball
+
+ vertSpeed =
+ if shouldBounceVertically then
+ ball.vertSpeed * -1
+
+ else
+ ball.vertSpeed
+ in
+ case gameStatus of
+ Winner _ ->
+ ball
+
+ NoWinner ->
+ { ball
+ | x = ball.x + horizSpeed
+ , y = ball.y + vertSpeed
+ , horizSpeed = horizSpeed
+ , vertSpeed = vertSpeed
+ }
+
+
updatePaddle : PaddleMovement -> Paddle -> Paddle
updatePaddle movement paddle =
let
That's a big one! It looks impressive, but most of it is just moving the code
related to updating the ball (checking if it bounces to update its speed and
moving it) to its own updateBall helper.
However there's something worth noting here, and it's in the signature of the
updateBall:
updateBall :
{ a
| gameStatus : GameStatus
, ball : Ball
, rightPaddle : Paddle
, leftPaddle : Paddle
}
-> Ball
updateBall { gameStatus, ball, rightPaddle, leftPaddle } =
Up til now we've seen how to write a type signature with various types, but
this is the first time we're seeing this { a | ...} notation. This is an
extensible record (more
information in
this "Advanced Types in Elm - Extensible Records" blog post by Charlie
Koster
and the
"Scaling elm apps" talk by Richard Feldman).
To sum it up, it's a way to
- document which fields are of interest to the function
- narrow the arguments to the function: it'll only take, use or return specific fields from the records
- make a function usable on several different types of records, as long as they have the fields defined in the extensible record
In our case we're only using this for the first two use cases.
We're now left with this game status and score update. Those two should obviously happen together, but it feels a bit alien to have them mixed in the game loop together with the updating of the paddles.
How awesome would it be to have a NewWinner Player message? If we had it, we
could update the game status and the score update in this case of the
update function, and it would make perfect sense!
"But Mathieu, how do we send our own messages to the update function?
Aren't messages usually coming from subscriptions, or maybe events like
onClick on a button and the like? We've always had those messages handed to
us by the elm runtime through the update function!".
Well, yes, usually the messages are provided, relayed by the elm runtime. And we could tell the runtime to send us such a message, but as you can read from this piece, it's not recommended (check "How to turn a Msg into a Cmd in Elm?" from Wouter In t Velt for more information on why).
But if we get back to the original question: how do we send our own messages to
the update function?
Well, the update function is just that: a function. And a function can be
called, for example with our own NewWinner Player message, and the updated
model we get in the "game loop":
@@ -63,6 +63,7 @@ type Msg
| KeyDown PlayerAction
| KeyUp PlayerAction
| SleepDone
+ | NewWinner Player
type PlayerAction
@@ -136,34 +137,32 @@ update msg model =
updatedBall =
updateBall model
- ( gameStatus, score, cmd ) =
- case ( maybeWinner updatedBall, model.gameStatus ) of
- ( Just player, NoWinner ) ->
- let
- alwaysSleepDone : a -> Msg
- alwaysSleepDone =
- always SleepDone
-
- delayCmd =
- Process.sleep 500
- |> Task.perform alwaysSleepDone
-
- updatedScore =
- updateScores model.score player
- in
- ( Winner player, updatedScore, delayCmd )
-
- _ ->
- ( model.gameStatus, model.score, Cmd.none )
+ updatedModel =
+ { model
+ | ball = updatedBall
+ , rightPaddle = updatePaddle model.rightPaddleMovement model.rightPaddle
+ , leftPaddle = updatePaddle model.leftPaddleMovement model.leftPaddle
+ }
in
- ( { model
- | ball = updatedBall
- , rightPaddle = updatePaddle model.rightPaddleMovement model.rightPaddle
- , leftPaddle = updatePaddle model.leftPaddleMovement model.leftPaddle
- , gameStatus = gameStatus
- , score = score
- }
- , cmd
+ case ( maybeWinner updatedBall, model.gameStatus ) of
+ ( Just player, NoWinner ) ->
+ update (NewWinner player) updatedModel
+
+ _ ->
+ ( updatedModel, Cmd.none )
+
+ NewWinner player ->
+ let
+ alwaysSleepDone : a -> Msg
+ alwaysSleepDone =
+ always SleepDone
+
+ updatedScore =
+ updateScores model.score player
+ in
+ ( { model | gameStatus = Winner player, score = updatedScore }
+ , Process.sleep 500
+ |> Task.perform alwaysSleepDone
)
KeyDown playerAction ->
What we did here is:
- in the game loop, update the ball and the paddles
- make an updated model with those updates
- if there's no new winner, return that updated model
- if there's a new winner, return the result of a call to the
updatefunction with ourNewWinner Playermessage and the updated model
While we're rewriting and refactoring parts of the update function, let's
rename this SleepDone message which isn't very meaningful to RestartGame
instead:
= OnAnimationFrame Float
| KeyDown PlayerAction
| KeyUp PlayerAction
- | SleepDone
+ | RestartGame
| NewWinner Player
@@ -153,16 +153,16 @@ update msg model =
NewWinner player ->
let
- alwaysSleepDone : a -> Msg
- alwaysSleepDone =
- always SleepDone
+ alwaysRestartGame : a -> Msg
+ alwaysRestartGame =
+ always RestartGame
updatedScore =
updateScores model.score player
in
( { model | gameStatus = Winner player, score = updatedScore }
, Process.sleep 500
- |> Task.perform alwaysSleepDone
+ |> Task.perform alwaysRestartGame
)
KeyDown playerAction ->
@@ -209,7 +209,7 @@ update msg model =
, Cmd.none
)
- SleepDone ->
+ RestartGame ->
( { model
| ball = initBall
, gameStatus = NoWinner
We're now in a much better place!
Non linear paddles
If we look back at the original gameplay we see that the ball doesn't bounce linearily on the paddles. Depending on where it touches the paddle, the bounce angle varies. This is better explained in this tutorial on writing a pong game in unity.
Let's implement that!
When we update the horizSpeed when the ball shouldBounce, we now also need
to update the vertSpeed according to the place where the ball hit the paddle.
The idea is to come up with a "distance" in signed percentage from the center of the paddle, so we would have -100% for a hit right on the top of the paddle, and 100% if it's the bottom of the paddle.
Once we have this percentage, we can divide it by 10 to have a vertical speed between 0 (the ball hits the paddle right in the center) and 10 (the ball hits the top or the bottom of the paddle).
Here's the modified updateBall function:
updateBall { gameStatus, ball, rightPaddle, leftPaddle } =
let
- shouldBounce =
- shouldBallBounce rightPaddle ball
- || shouldBallBounce leftPaddle ball
+ maybeRightDistance =
+ maybeBounceDistanceFromCenter rightPaddle ball
- horizSpeed =
- if shouldBounce then
- ball.horizSpeed * -1
+ maybeLeftDistance =
+ maybeBounceDistanceFromCenter leftPaddle ball
+
+ maybeDistance =
+ -- Combine the two maybes and keep the one that isn't Nothing, if any.
+ if maybeRightDistance == Nothing then
+ maybeLeftDistance
else
- ball.horizSpeed
+ maybeRightDistance
+
+ ( horizSpeed, bouncedVertSpeed ) =
+ case maybeDistance of
+ Nothing ->
+ -- No bounce
+ ( ball.horizSpeed, ball.vertSpeed )
+
+ Just distance ->
+ ( ball.horizSpeed * -1
+ , distance // 10
+ )
shouldBounceVertically =
shouldBallBounceVertically ball
vertSpeed =
if shouldBounceVertically then
- ball.vertSpeed * -1
+ bouncedVertSpeed * -1
else
- ball.vertSpeed
+ bouncedVertSpeed
in
case gameStatus of
Winner _ ->
Nothing fancy here appart from the maybeDistance: we "combine" both Maybes
by keeping the first one that isn't a Nothing if any. This way we simplify
the case maybeDistance and we don't have to duplicate the code that updates
the horizSpeed and vertSpeed if there's a hit on the left or right paddle.
Now for the hairy maybeBounceDistanceFromCenter:
-shouldBallBounce : Paddle -> Ball -> Bool
-shouldBallBounce paddle ball =
+maybeBounceDistanceFromCenter : Paddle -> Ball -> Maybe Int
+maybeBounceDistanceFromCenter paddle ball =
+ -- If the ball bounces, return Just the distance from the paddle center in
+ -- percentage, so -100% if it's the very top of the paddle, 100% if it's
+ -- the very bottom of the paddle.
+ let
+ normalize : Int -> Int -> Int
+ normalize distance height =
+ (distance - (height // 2)) * 100 // (height // 2)
+ in
case paddle of
LeftPaddle { x, y, width, height } ->
- (ball.x - ball.radius <= x + width)
- && (ball.y >= y)
- && (ball.y <= y + height)
- && (ball.horizSpeed < 0)
+ if
+ (ball.x - ball.radius <= x + width)
+ && (ball.y >= y)
+ && (ball.y <= y + height)
+ && (ball.horizSpeed < 0)
+ then
+ Just <| normalize (ball.y - y) height
+
+ else
+ Nothing
RightPaddle { x, y, height } ->
- (ball.x + ball.radius >= x)
- && (ball.y >= y)
- && (ball.y <= y + height)
- && (ball.horizSpeed > 0)
+ if
+ (ball.x + ball.radius >= x)
+ && (ball.y >= y)
+ && (ball.y <= y + height)
+ && (ball.horizSpeed > 0)
+ then
+ Just <| normalize (ball.y - y) height
+
+ else
+ Nothing
Phew, that was a tough one, but we did it!
Cosmetic changes
Well, it seems we're nearly done! By looking at the original pong we can see there's a couple of obvious differences still: the ball should be square (which will make this issue disappear), and there's a dotted line in the center of the screen.
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ type alias Model =
type alias Ball =
{ x : Int
, y : Int
- , radius : Int
+ , size : Int
, horizSpeed : Int
, vertSpeed : Int
}
@@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ initBall : Ball
initBall =
{ x = 250
, y = 250
- , radius = 10
+ , size = 10
, horizSpeed = 4
, vertSpeed = 2
}
@@ -321,7 +321,7 @@ maybeBounceDistanceFromCenter paddle ball =
case paddle of
LeftPaddle { x, y, width, height } ->
if
- (ball.x - ball.radius <= x + width)
+ (ball.x <= x + width)
&& (ball.y >= y)
&& (ball.y <= y + height)
&& (ball.horizSpeed < 0)
@@ -333,7 +333,7 @@ maybeBounceDistanceFromCenter paddle ball =
RightPaddle { x, y, height } ->
if
- (ball.x + ball.radius >= x)
+ (ball.x + ball.size >= x)
&& (ball.y >= y)
&& (ball.y <= y + height)
&& (ball.horizSpeed > 0)
@@ -347,18 +347,18 @@ maybeBounceDistanceFromCenter paddle ball =
shouldBallBounceVertically : Ball -> Bool
shouldBallBounceVertically ball =
let
- radius =
- ball.radius
+ size =
+ ball.size
in
- ball.y <= radius || ball.y >= (500 - radius)
+ ball.y <= size || ball.y >= (500 - size)
maybeWinner : Ball -> Maybe Player
maybeWinner ball =
- if ball.x <= ball.radius then
+ if ball.x <= ball.size then
Just RightPlayer
- else if ball.x >= (500 - ball.radius) then
+ else if ball.x >= (500 - ball.size) then
Just LeftPlayer
else
@@ -391,11 +391,12 @@ view { ball, rightPaddle, leftPaddle, score } =
viewBall : Ball -> Svg.Svg Msg
-viewBall { x, y, radius } =
- circle
- [ cx <| String.fromInt x
- , cy <| String.fromInt y
- , r <| String.fromInt radius
+viewBall ball =
+ rect
+ [ x <| String.fromInt ball.x
+ , y <| String.fromInt ball.y
+ , width <| String.fromInt ball.size
+ , height <| String.fromInt ball.size
]
[]
We renamed the radius field of the Ball record to be size instead which
makes more sense for a square ball, and updated the viewBall helper to draw a
rect instead of a circle. We also took the opportunity to fix a small bug, did
you spot it?
Yes, we were checking for ball.x - ball.radius for the left paddle... which
meant we were bouncing the ball from the left paddle 10 pixels too early.
And for the screen divider:
@@ -383,13 +383,28 @@ view { ball, rightPaddle, leftPaddle, score } =
, viewBox "0 0 500 500"
, Svg.Attributes.style "background: #efefef"
]
- [ viewBall ball
+ [ viewDivider
+ , viewBall ball
, viewPaddle rightPaddle
, viewPaddle leftPaddle
, viewScore score
]
+viewDivider : Svg.Svg Msg
+viewDivider =
+ line
+ [ x1 "249"
+ , y1 "0"
+ , x2 "249"
+ , y2 "500"
+ , stroke "black"
+ , strokeDasharray "4"
+ , strokeWidth "2"
+ ]
+ []
+
+
viewBall : Ball -> Svg.Svg Msg
viewBall ball =
rect
And a final touch: let's move the scores closer to their edges:
@@ -442,9 +442,9 @@ viewScore score =
[ fontSize "100px"
, fontFamily "monospace"
]
- [ text_ [ x "100", y "100", textAnchor "start" ]
+ [ text_ [ x "50", y "100", textAnchor "start" ]
[ text <| String.fromInt score.leftPlayerScore ]
- , text_ [ x "400", y "100", textAnchor "end" ]
+ , text_ [ x "450", y "100", textAnchor "end" ]
[ text <| String.fromInt score.rightPlayerScore ]
]
And now we have it:
Randomizing the game restart
Whenever the game (re)starts the ball always has the exact same direction. It would be nice to have some sort of randomization: in the original gameplay, it seems that the ball is aimed at the last loser, and the starting height and direction are random.
So let's use the
elm/random package!
It should be very straightforward, just calling the equivalent of Math.random
in javascript right?
Wrong.
I know what you're thinking: "this elm thing is such a downer, always in my way, always restricting what I can and can't do and all that crap!". And I feel you. However let's not lose track of the upsides. Every programming language that I know of is a compromise between upsides and downsides.
Sure, the pure functional part of elm can be a pain (wait, no side effects? How are people meant to achieve anything without side effects? In elm the side effects only happen in the elm runtime), but it's also the best part in my humble opinion. Not having to worry about hidden side effects is a blessing.
So anyway, back to the point: getting a random number without an initial seed
is impure (every time you call Math.random() you have a different result).
And in elm everything is pure. "Pure" meaning that a function call with the
same arguments will always return the exact same result. Which means there's no
side effects.
With a seed though, it's entirely different: a random number generator will always give the same result for a given seed, so it's pure.
So we have two ways to get a random number in elm
- send a
Cmd Msgto the elm runtime, and "receive" it through aMsg - query a number directly by providing a seed
Let's try the first one, and see how it goes:
import Browser.Events
import Json.Decode as Decode
import Process
+import Random
import Svg exposing (..)
import Svg.Attributes exposing (..)
import Task
@@ -64,6 +65,7 @@ type Msg
| KeyUp PlayerAction
| RestartGame
| NewWinner Player
+ | NewDirection Int
type PlayerAction
@@ -159,12 +161,25 @@ update msg model =
updatedScore =
updateScores model.score player
+
+ sleepCmd =
+ Process.sleep 500
+ |> Task.perform alwaysRestartGame
in
( { model | gameStatus = Winner player, score = updatedScore }
- , Process.sleep 500
- |> Task.perform alwaysRestartGame
+ , Cmd.batch
+ [ sleepCmd
+ , Random.generate NewDirection (Random.int 0 100)
+ ]
)
+ NewDirection direction ->
+ let
+ _ =
+ Debug.log "New random direction" direction
+ in
+ ( model, Cmd.none )
+
KeyDown playerAction ->
case playerAction of
RightPaddleUp ->
Also let's not forget to install the Random package:
$ elm install elm/random
Which results in this modification in the elm.json file:
"elm/core": "1.0.2",
"elm/html": "1.0.0",
"elm/json": "1.1.3",
+ "elm/random": "1.0.0",
"elm/svg": "1.0.1"
},
"indirect": {
This works like a charm, we do have random directions in the console output:

The code is pretty straightforward and easy to understand, but wait a minute: when will we use this random number? I mean, it would be a pity if the sleep was expired already, and the game restarted, before we get the new direction.
The easy way to "synchronize" this is to first query the new random direction, and then when dealing with the reception of that random number, start the sleep. This way we're sure it's done in the right order. It does mean we'll have two messages that are tied together, linked, which feels a bit artifical, awkward, even though it's doable and wouldn't be that bad.
Still, let's try the other solution, just to see what it looks like. We'll use
Random.step
which needs a Seed. But the only way we can create a Seed is with
Random.initialSeed
which takes... a number.
Ok, but where does this number come from? Let's deal with that later, and use a
perfectly fine number for now: 42
@@ -65,7 +65,6 @@ type Msg
| KeyUp PlayerAction
| RestartGame
| NewWinner Player
- | NewDirection Int
type PlayerAction
@@ -165,21 +164,16 @@ update msg model =
sleepCmd =
Process.sleep 500
|> Task.perform alwaysRestartGame
+
+ ( randomDirection, _ ) =
+ Random.initialSeed 42
+ |> Random.step (Random.int 0 100)
+ |> Debug.log "Random direction: "
in
( { model | gameStatus = Winner player, score = updatedScore }
- , Cmd.batch
- [ sleepCmd
- , Random.generate NewDirection (Random.int 0 100)
- ]
+ , sleepCmd
)
- NewDirection direction ->
- let
- _ =
- Debug.log "New random direction" direction
- in
- ( model, Cmd.none )
-
KeyDown playerAction ->
case playerAction of
RightPaddleUp ->
And we now have the following console logs:

So far, we don't have any randomness in the numbers we're getting... but that's
expected, because we're always using the same exact Seed based on the same
exact number: 42.
The cool thing with Random.step is that it gives you a new seed together with
the random number you asked. So if we could store this new seed in the model
and use that on the next call, we'd have a series of different random number:
@@ -18,6 +18,7 @@ type alias Model =
, leftPaddleMovement : PaddleMovement
, gameStatus : GameStatus
, score : Score
+ , seed : Random.Seed
}
@@ -96,6 +97,7 @@ init _ =
{ rightPlayerScore = 0
, leftPlayerScore = 0
}
+ , seed = Random.initialSeed 42
}
, Cmd.none
)
@@ -165,12 +167,16 @@ update msg model =
Process.sleep 500
|> Task.perform alwaysRestartGame
- ( randomDirection, _ ) =
- Random.initialSeed 42
+ ( randomDirection, newSeed ) =
+ model.seed
|> Random.step (Random.int 0 100)
|> Debug.log "Random direction: "
in
- ( { model | gameStatus = Winner player, score = updatedScore }
+ ( { model
+ | gameStatus = Winner player
+ , score = updatedScore
+ , seed = newSeed
+ }
, sleepCmd
)
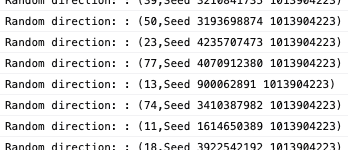
"But Mathieu, that's not really random, we're always using the same seed to initialize the generator, so we'll always have the exact same number sequence whenever we reload the page!". That's true. We're using a fixed seed whenever we start the game so this means players could theoretically remembers the sequence.
This could be fixed using several techniques:
- Use
Random.generatethe first time to initialize the seed when the game start - Use the timestamp of the current time when the program starts
- Use a randomly generated number that was passed to the elm program
The first two solutions are basically the same: in the init send a command to
get a random number or the current timestamp, store that in the model as the
seed, and use that from then on. They also both have kind of the same problem
as we saw previously: there's some synchronisation issue. What happens if the
first game restart happens before we got the random number or timestamp back
from the elm runtime? This is obviously very unlikely, especially in our use
case. And we could also decide that it's not a big deal, and use that.
But as we're going through a series of blog posts that are dedicated to
learning elm, let's take this opportunity to talk about the third solution:
it's based on the javascript
interop, and specifically the
flags in our case.
Using flags
Flags are a way to pass
initial data from javascript to the elm program. This would be a perfect tool
for our use case: Call Math.random() in javascript, then pass that initial
seed to the elm program on startup. And from then on use this seed to get new
random numbers (and new seeds, and so on).
But before we can use flags, we need a bit of setup. Up til now we used an
automatically generated index.html file containing the inline javascript code
compiled from our elm code. But this means we can't modify the initialization
code as it would be overwritten each and every time we could compile again.
So we need to generate an index.html file that imports the generated
javascript, and a piece of javascript code that initializes the elm program.
Let's base our new index.html file on the example from the interop
documentation:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Elm pong</title>
<script src="app.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="elm"></div>
<script>
var app = Elm.Main.init({
node: document.getElementById('elm')
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
We also need to change the scripts entries in the package.json file.
You'll see all of that in the
commit.
We can now change the initialization script so it passes flags to elm.
Tiny step: let's first pass the number 42 from the javascript side:
The index.html file:
<div id="elm"></div>
<script>
var app = Elm.Main.init({
- node: document.getElementById('elm')
+ node: document.getElementById('elm'),
+ flags: 42
});
</script>
</body>
And the src/Main.elm file:
@@ -82,11 +82,11 @@ type alias Score =
type alias Flags =
- ()
+ Int
init : Flags -> ( Model, Cmd Msg )
-init _ =
+init seed =
( { ball = initBall
, rightPaddle = RightPaddle <| initPaddle 480
, leftPaddle = LeftPaddle <| initPaddle 10
@@ -97,7 +97,7 @@ init _ =
{ rightPlayerScore = 0
, leftPlayerScore = 0
}
- , seed = Random.initialSeed 42
+ , seed = Random.initialSeed seed
}
, Cmd.none
)
What that says is we now care very much about the Flags passed to the init
function, as we're using it to initialize our seed.
So the Flags type isn't the unit anymore (remember, the type that we
usually use in place of values we don't care about), but an Int to hold our
seed. It could be a Record, a String, a Bool, a JSON value or any other
of the base types in elm.
Next tiny step: generate a proper random number on the javascript side, and
pass it to our elm program instead of the number 42.
Our index.html file should be modified this way:
<body>
<div id="elm"></div>
<script>
+ let seed = Math.random() * 100; // A random number between 0 and 100.
var app = Elm.Main.init({
node: document.getElementById('elm'),
- flags: 42
+ flags: Math.round(seed)
});
</script>
</body>
We need to Math.round() the result as otherwise it would be a float and not
an integer.
And now, every time we refresh the page, we can see that the sequence of random numbers is different! We did it!
By the way if we write elm in the first place, it's to write as little javascript as possible. So maybe we should change the javascript to simply pass the raw random number which is a float between 0 and 1, and deal with the rest on the elm side?
Simplify the index.html:
<body>
<div id="elm"></div>
<script>
- let seed = Math.random() * 100; // A random number between 0 and 100.
+ let seed = Math.random();
var app = Elm.Main.init({
node: document.getElementById('elm'),
- flags: Math.round(seed)
+ flags: seed
});
</script>
And the src/Main.elm file:
type alias Flags =
- Int
+ Float
init : Flags -> ( Model, Cmd Msg )
@@ -97,7 +97,13 @@ init seed =
{ rightPlayerScore = 0
, leftPlayerScore = 0
}
- , seed = Random.initialSeed seed
+ , seed =
+ -- A number between 0 and 100
+ seed
+ |> (*) 100
+ |> round
+ |> Random.initialSeed
}
, Cmd.none
)
Keep in mind that here we convert the float between 0 to 1 to an integer
between 0 to 100. We could do whatever we want here, for example convert it to
be between 0 and 10000 to have more seeds. Or we could ditch Math.random()
entirely and use the current timestamp.
So anyway, now that we have our seed, what kind of random numbers are we going
to generate, and for what usage? Well, in the updateBall helper we decided
that the vertical speed was going to be between -10 and +10. So let's
initialize our ball vertSpeed this way:
+randomVertSpeed : Random.Seed -> ( Int, Random.Seed )
+randomVertSpeed seed =
+ Random.step (Random.int -10 10) seed
+
+
init : Flags -> ( Model, Cmd Msg )
init seed =
- ( { ball = initBall
+ let
+ initialSeed =
+ -- A number between 0 and 100
+ seed
+ |> (*) 100
+ |> round
+ |> Random.initialSeed
+
+ ( initialVertSpeed, newSeed ) =
+ randomVertSpeed initialSeed
+
+ initialBall =
+ { initBall | vertSpeed = initialVertSpeed }
+ in
+ ( { ball = initialBall
, rightPaddle = RightPaddle <| initPaddle 480
, leftPaddle = LeftPaddle <| initPaddle 10
, rightPaddleMovement = NotMoving
@@ -97,12 +116,7 @@ init seed =
{ rightPlayerScore = 0
, leftPlayerScore = 0
}
- , seed =
- -- A number between -100 and 100
- seed
- |> (*) 100
- |> round
- |> Random.initialSeed
+ , seed = newSeed
}
, Cmd.none
)
So we created a small randomVertSpeed helper, and using the initial seed we
compute from the javascript value, we set the initial ball's vertSpeed.
And now we want to also use a random vertical seed on each game restart:
@@ -185,16 +185,10 @@ update msg model =
sleepCmd =
Process.sleep 500
|> Task.perform alwaysRestartGame
-
- ( randomDirection, newSeed ) =
- model.seed
- |> Random.step (Random.int 0 100)
- |> Debug.log "Random direction: "
in
( { model
| gameStatus = Winner player
, score = updatedScore
- , seed = newSeed
}
, sleepCmd
)
@@ -244,9 +238,17 @@ update msg model =
)
RestartGame ->
+ let
+ ( vertSpeed, newSeed ) =
+ randomVertSpeed model.seed
+
+ ball =
+ { initBall | vertSpeed = vertSpeed }
+ in
( { model
- | ball = initBall
+ | ball = ball
, gameStatus = NoWinner
+ , seed = newSeed
}
, Cmd.none
)
We moved the new vertical speed generation and the seed updating code to the
RestartGame were we also initialized the ball.
This is coming alone just perfectly!
Maybe a last addition: let's shoot the ball towards the last loser
( vertSpeed, newSeed ) =
randomVertSpeed model.seed
+ horizSpeedDirection =
+ -- This number is either 1 if the loser is the right
+ -- player, or -1 if it's the left player who lost last.
+ case model.gameStatus of
+ Winner RightPlayer ->
+ -1
+
+ _ ->
+ -- Here we are returning 1 if it's the LeftPlayer,
+ -- and at the same time dealing with the `NoWinner`
+ -- case which shouldn't happen.
+ 1
+
ball =
- { initBall | vertSpeed = vertSpeed }
+ { initBall
+ | vertSpeed = vertSpeed
+ , horizSpeed = initBall.horizSpeed * horizSpeedDirection
+ }
in
( { model
| ball = ball
And we have now completed our game, and this series of blog posts!
If you've followed along during those four episodes, thanks for your patience! I hope that those have been useful to you, and feel free to reach out via email, twitter or on the elm slack.